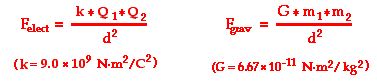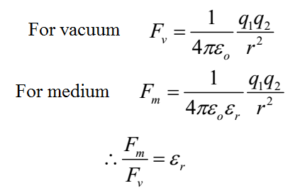K Value In Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest.
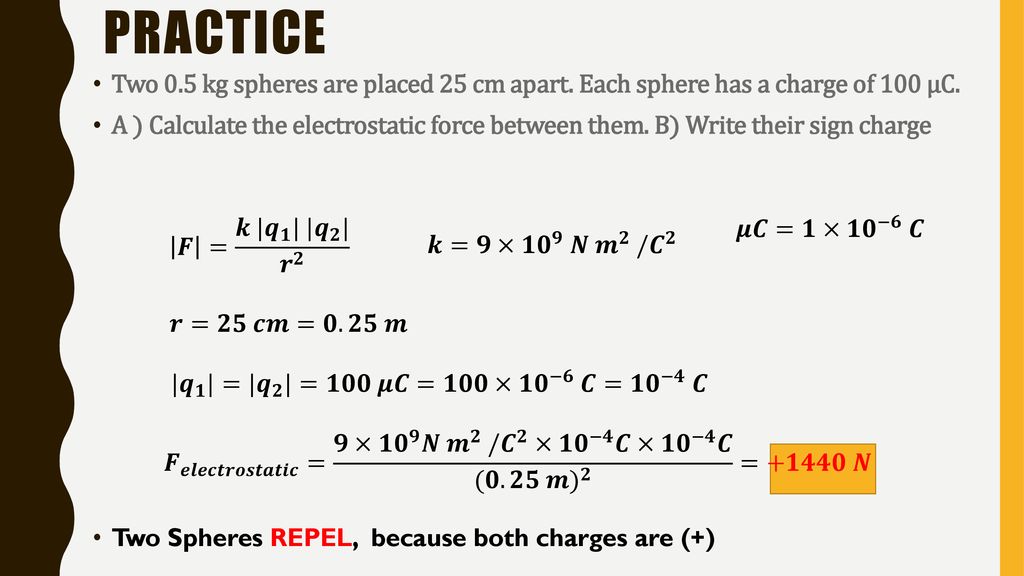
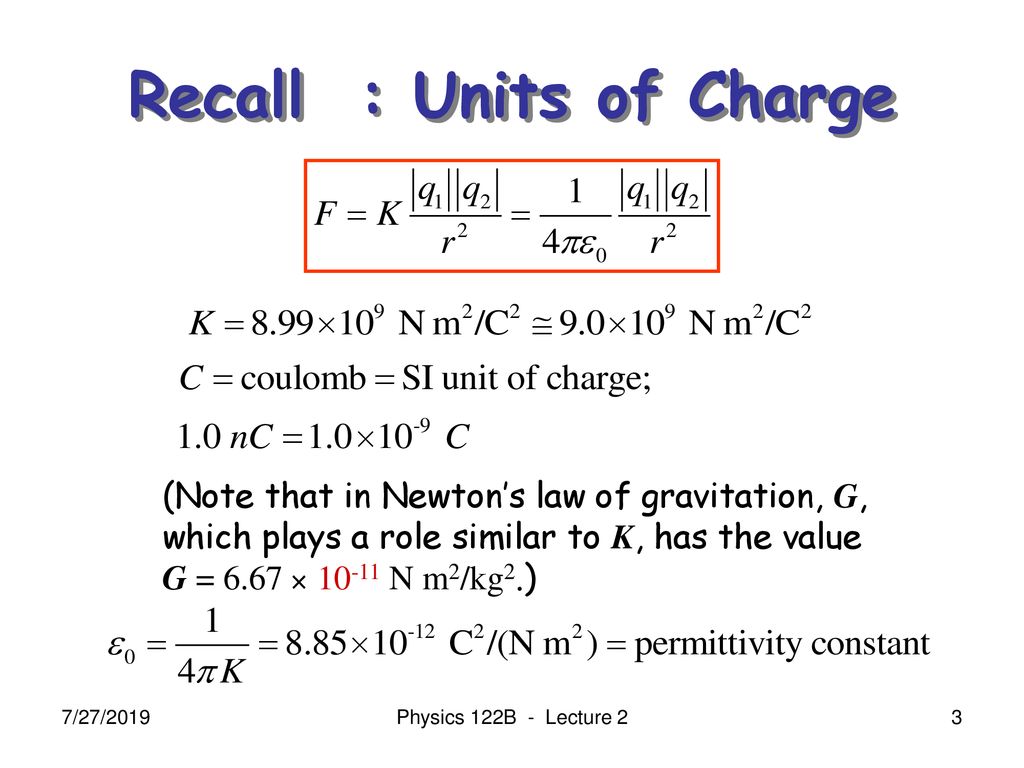
K value in electrostatics. The force of the interaction between the charges is attractive if the charges have opposite signs i e f is negative and repulsive if like signed i e f is positive. In physics electrostatics deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow moving electric charges. Where ke is coulomb s constant ke 8 99 109 n m2 c 2 7 q1 and q2 are the signed magnitudes of the charges and the scalar r is the distance between the charges. K value is an indicator of molecular weight.
K e electrostatic constant 8 99 10 9 n m 2 c 2 ε 0 vacuum permittivity 8 85 10 12 c 2 n m 2 text when two charges have the same sign their. Value of k units 8 987 551 7923 14 10 9 n m 2 c 2 14 3996 ev å e 2 10 7 n s 2 c 2 c 2 the coulomb constant the electric force constant or the electrostatic constant denoted k e k or k is a proportionality constant in electrostatics equations. If the medium between the charges is space or air then the value of k in si is 9 x10 9 nm 2 c 2. K 57 is medium for injection molding k 67 is medium high for rigid extrusion k 70 is higher for plasticized extrusion or calendering.
So the lower the k the better the insulator. In the case of free. The electric field of the charge causes polarization. Styrofoam peanuts clinging to a cat s fur due to static electricity.
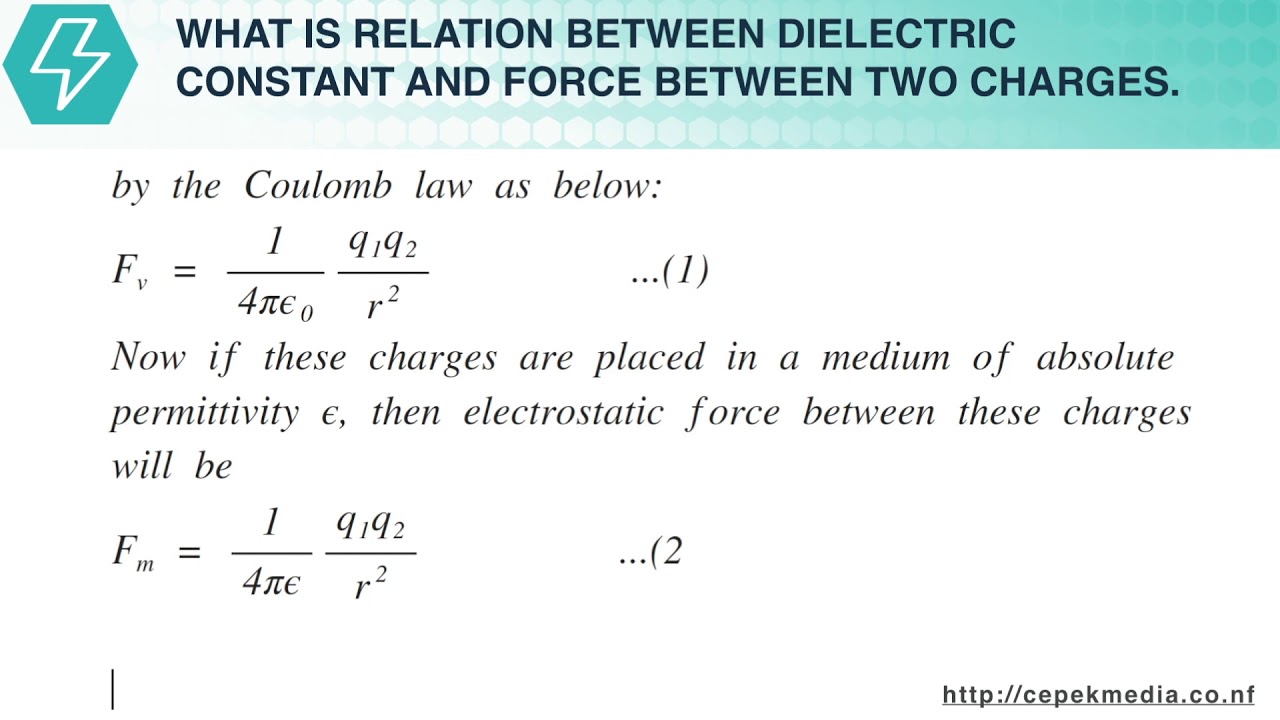
In order to show the dependence of k upon the medium it is usually expressed in terms of the property of that medium known as permittivity. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other and are described by coulomb s law even though. The triboelectric effect causes an electrostatic charge to build up on the surface of the fur due to the cat s motions.